Memcached and Redis are the leading names as caching systems, serving as important tools for optimizing data retrieval and storage in modern applications. Both Memcached and Redis share a common goal of enhancing system performance and scalability, thereby playing an important role in the seamless handling of data.
However, apart from their shared goals, both platforms differ significantly in terms of distinctive features and functionalities that set Memcached and Redis apart. We have differentiated both systems in terms of their strengths and weaknesses, architectural variances, and performance attributes.
Memcached vs Redis: Overview
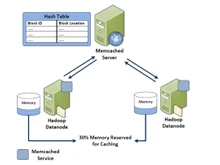
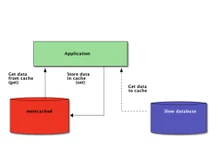
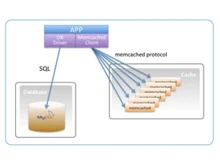
Memcached is a high-performance, distributed memory caching system that is designed to accelerate dynamic web applications. It functions by storing frequently accessed data in memory, thereby reducing the need for repeated database queries, and boosting the overall system responsiveness.
However, Redis is a highly advanced key-value store that has emerged as a leading player in data management and caching. Known for its lightning-fast performance, Redis excels in the seamless handling of real-time applications with low-latency requirements.
Between Memcached and Redis, Memcached is known for its straightforward caching mechanism. Redis, on the other hand, stands out for its versatile data structures and advanced features, thereby making it a perfect choice for applications that require more than the basic caching functionality.
Memcached vs Redis: Pros & Cons
- Redis offers support for multiple data types, including strings, hashes, bitmaps, hyperlogs, and more. Memcached on the other hand, does not support as many data types as Redis.
- Redis is designed to be simple, fast, and efficient. On the contrary, Memcached is not a difficult application to use, but it is not as simple as Redis.
- Memcached does not offer support for persistence operations, whereas Redis provides several operations when it comes to persistence. These include RDB, AOF, No Persistence, and RDB+AOF.
- Based on the multi-threading parameter, Redis offers robust support for multi-threading, while Memcached does not support multi-threading.
Redis and Memcached - In Terms of Features
- Persistence: Memcached is a pure caching system, and it does not offer any built-in persistence. All the data is stored in the memory and is lost in the event of a restart or a failure. Redis, however, supports in-memory storage and optional disk persistence. You can easily configure Redis to reduce the risk of data loss.
- Atomic Operations: Memcached offers support for basic atomic operations such as increment and decrement on numeric values associated with the keys. However, unlike Memcached, the atomic operations offered by Redis are much more dynamic and they help with sophisticated manipulations.
- Replication: Redis provides in-built replication that helps in the automatic synchronization of data across multiple instances within a cluster. This, in turn, enhances fault tolerance and ensures high availability. In contrast, Memcached lacks built-in replication features, which makes it less suitable for applications that require a high level of availability.
- Language Support: Redis boasts an extensive range of language support, featuring client libraries for different programming languages, including Python, Java, .NET, and Ruby. On the other hand, Memcached also offers good language support, but it is not as extensive as Redis.
Redis and Memcached: Ease of Use
Memcached and Redis are both easy to use, with simple commands that are easy to understand as well as implement. However, Redis has better documentation and is more user-friendly compared to Memcached, thereby making it easy for the developers to get started and troubleshoot their issues with ease.
Memcached vs Redis: Scalability
Memcached and Redis are both designed and built to be scalable, and they can be easily deployed in a distributed environment. However, Memcached is better suited for horizontal scaling, where multiple servers are used to handle the increasing load of traffic. In contrast, Redis will be an ideal choice for vertical scaling, where a single server can be easily scaled to handle the traffic.
Memcached vs Redis: Data Structure Handling
Both Memcached and Redis serve as important key-value stores, but Redis provides a comprehensive range of data structures, including lists, sets, and hashes. These structures will enable the users to store more complex data and manipulate it easily. On the other hand, Memcached offers support for only simple key-value pairs, which makes it less flexible for complex data handling.
Redis and Memcached: Performance
Memcached is designed to be a lightweight caching solution with a simple caching algorithm that makes it an effective choice in reducing the overall database load. Redis, on the other hand, supports higher performance, especially when it comes to heavy applications.
Which is Better, Memcached or Redis?
Redis outshines Memcached in various important areas, making it an ideal choice for most users. First and foremost, Redis offers support for multiple data types, unlike Memcached, so it becomes easy for the user to store complex data with ease. In addition, Redis provides several operations when it comes to persistence. These include RDB, AOF, No Persistence, and RDB+AOF.
However, Memcached shines under the performance parameter. Memcached is designed to serve as a lightweight caching solution featuring a straightforward caching algorithm.


 6 Ratings & 0 Reviews
6 Ratings & 0 Reviews