Hazelcast and Redis are two prominent data storage and computing solutions. In this write-up, we will be comparing these two solutions based on their fundamental differences such as threading, clustering, compute functions, and other important features. Through this, you would be able to understand the concepts of in-memory data handling, distributed computing, scalability, and others. This comparison will serve as a guide to analyze the advantages of each platform. Let’s see the detailed comparison.
Hazelcast vs. Redis: An Overview
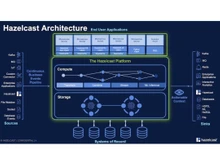
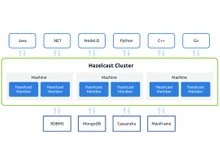
Hazelcast is an open-source, in-memory data grid and computing platform that provides distributed data storage and parallel processing capabilities. It is designed to handle large volumes of data with high throughput and low latency, offering scalable and fault-tolerant solutions for caching, data distribution, and real-time processing. Hazelcast allows seamless integration into existing applications and supports various programming languages. It offers clustering and automatic failover mechanisms to ensure high availability, distributed data structures, and querying capabilities.
On the other hand, Redis is an open-source, high-performance, in-memory data structure store used as a caching layer, message broker, and data store. It is known for its versatility in handling various data structures like strings, lists, sets, hashes, and more. This allows for data manipulation and storage. Apart from that, Redis is known for its low-latency access, which makes it ideal for time-sensitive applications such as real-time analytics, session storage, and queuing systems. Moreover, it also offers built-in replication, clustering, and persistence options for scaling and securing data-intensive applications.
Hazelcast vs. Redis: Key Differences
Here are a few key differences between Hazelcast and Redis:
- Hazelcast and a few Hazelcast alternatives use multithreading for concurrent processing and distributed data handling. While Redis is single-threaded but manages multiple connections through a single event loop.
- Hazelcast supports dynamic clustering and automatic discovery of cluster members for scalability. On the other hand, Redis also supports clustering but requires manual sharding for distributing data across multiple nodes.
- Hazelcast supports distributed computing through its compute grid, enabling parallel execution of tasks across the cluster. However, Redis and other Redis alternatives don’t offer built-in distributed computing features.
Hazelcast and Redis: In Terms of Features
Below are some of the key feature differentiations between Hazelcast and Redis. These include querying, data backup, failure detection, threading, and more.
- Querying: Hazelcast allows querying of distributed data using its own query language, Predicates, or SQL for real-time data analysis. On the other hand, Redis provides limited querying capabilities through commands such as SCAN and keys, but it is primarily designed for key-value data storage.
- Streaming: Hazelcast provides a Jet streaming module for real-time data processing and stream processing. Redis, on the other hand, does not have native streaming capabilities but can be integrated with other streaming frameworks.
- Data Backup: Hazelcast allows for data backups through its built-in backup and WAN replication features, ensuring data durability and disaster recovery. On the other hand, Redis provides data persistence to disk through snapshots and append-only files (AOF), enabling data backup and recovery.
- Failure Detection: Hazelcast offers an advanced failure detection mechanism to detect and handle node failures or network partitions. Redis also has mechanisms to handle node failures, but it requires manual intervention in certain cases.
Hazelcast vs. Redis: Clustering
Hazelcast supports dynamic clustering and automatic discovery of cluster members, providing high availability and scalability through seamless addition and removal of nodes. Redis also supports clustering but requires manual sharding to distribute data across multiple nodes.
Hazelcast or Redis: Memory Management
Hazelcast features a sophisticated memory management system with the ability to control data partitioning, eviction policies, and data expiration. Redis provides configurable memory policies, and eviction strategies, and supports data persistence to disk.
Hazelcast and Redis: Compute Functions
Hazelcast provides support for distributed computing through its compute grid, allowing parallel execution of tasks across the cluster. Redis primarily focuses on data storage and retrieval and does not offer built-in distributed computing functions.
Hazelcast and Redis: Language Written In
Hazelcast is written in Java, but it provides client libraries for various languages including Java, C#, C++, Python, and others. Redis is however written in C, but it also offers client libraries for several programming languages.
Hazelcast or Redis: Standard Serialization
Hazelcast provides support for standard serialization formats such as Java Serialization, Identified Data Serializable, and Portable Serialization. On the other hand, Redis supports various serialization formats including JSON, MessagePack, and others, and allows custom serialization/deserialization.
Verdict: Hazelcast vs. Redis
In conclusion, Hazelcast excels in its support for multithreading, dynamic clustering with automatic node discovery, and distributed computing capabilities through its compute grid. On the other hand, Redis stands out for its efficient single-threaded architecture, versatile data structures, and adoption as a caching layer, message broker, and data store. Both platforms offer scalable, high-performance in-memory data storage with replication and clustering support.


 4 Ratings & 0 Reviews
4 Ratings & 0 Reviews