ScyllaDB and Cassandra stand out as two leading choices for NoSQL databases, each renowned for their ability to handle massive amounts of data and ensure high availability and fault tolerance. In this comparison, we'll delve into the nuances of ScyllaDB versus Cassandra across various aspects, helping businesses make informed decisions about their database solutions.
ScyllaDB vs. Cassandra: Overview
ScyllaDB and Cassandra are distributed NoSQL databases built to handle large-scale data workloads. ScyllaDB is known for its exceptional performance and efficiency to achieve high throughput and low latency.
On the other hand, Cassandra, initially developed by Facebook and now maintained by the Apache Software Foundation, offers a highly scalable and fault-tolerant distributed database solution, and it is primarily written in Java.
ScyllaDB vs. Cassandra: Pros and Cons
- ScyllaDB boasts significantly higher read/write throughput and lower latencies compared to Cassandra due to its asynchronous architecture and modern hardware optimizations.
- Compared to ScyllaDB, Cassandra generally shows slower read/write speeds and higher latency, which is crucial for application responsiveness.
- ScyllaDB has some special features that Apache Cassandra doesn't have such as Incremental Compaction and Workload Prioritization. These features are helpful for achieving better performance and handling more data easily.
ScyllaDB vs. Cassandra: In Terms of Features
- Language: One major difference between ScyllaDB and Cassandra is that ScyllaDB is written in C++ programming language whereas Cassandra is written in Java.
- Supported Data Structures: Both support wide-column stores where data is organized by rows and columns. ScyllaDB offers additional support for super columns which allows for nested data structures within a column family. This is an advantage for complex data modeling. Cassandra on the other hand, focuses more on a simpler wide-column model without nested structures.
- I/O Model: ScyllaDB uses an asynchronous, non-blocking I/O model which helps in minimizing overhead loads and maximizing concurrency. This ensures better responsiveness under heavy loads. Whereas Cassandra primarily uses a synchronous I/O model which does not offer the same level of responsiveness under high concurrency.
- Integration: Cassandra offers a mature ecosystem of tools, libraries, and community support, including data modeling tools and monitoring solutions. It can also integrate with popular frameworks like Apache Spark and Apache Kafka. While ScyllaDB's ecosystem is growing, it may not offer the same level of tooling and integration options as Cassandra.
- Secondary Indexing: ScyllaDB supports secondary indexing through its global secondary indexes (GSI) feature, allowing users to query their data based on non-primary key columns efficiently. On the other hand, Cassandra provides Local Secondary Indexes (LSI) for secondary indexing. While LSIs can be fast for small datasets, they often become bottlenecks and hinder scalability with large data volumes.
ScyllaDB vs. Cassandra: Performance and Scalability
ScyllaDB and some other ScyllaDB alternatives are built for maximum performance as they work on a C++ codebase, modern hardware optimizations, and an efficient partitioning strategy. Its high throughput and low-latency capabilities make it a preferred choice for applications demanding exceptional performance. Cassandra, while also designed for scalability, often encounters performance bottlenecks with increasing data size and workload complexity.
ScyllaDB vs. Cassandra: Query Language
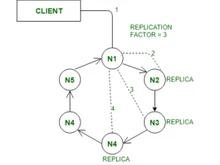
Both ScyllaDB and Cassandra follow the decentralized masterless architecture and utilize the Cassandra Query Language (CQL) for data manipulation. They support a flexible schema design that enables developers to adapt to evolving application needs seamlessly. However, ScyllaDB offers some extensions to the standard CQL for secondary indexes, version support, and counters that Cassandra doesn't support.
ScyllaDB vs. Cassandra: Ease of Use
ScyllaDB offers a more streamlined administration experience compared to Cassandra, with features like automatic data distribution and repair, simplified configuration options, and comprehensive monitoring and management tools. Cassandra, which is highly scalable and fault-tolerant, often requires more manual intervention and tuning to optimize performance and maintain cluster health.
ScyllaDB vs. Cassandra: Support
Cassandra and a few Cassandra alternatives offer a large and active community of users, developers, and contributors, providing extensive documentation, forums, and community-driven resources for learning and troubleshooting. ScyllaDB also has a growing community and provides dedicated support through its subscription offerings, including technical support, training, and consulting services.
ScyllaDB vs. Cassandra: Use Cases
ScyllaDB finds applications in various industries, including finance, e-commerce, and IoT, where high throughput and low latency are paramount. Its performance benefits make it well-suited for real-time analytics, time-series data processing, and high-volume transactional workloads. Similarly, Cassandra powers mission-critical applications in sectors such as social media, telecommunications, and healthcare, where scalability and fault tolerance are essential.
Which is Better: ScyllaDB or Cassandra
Both ScyllaDB and Cassandra are powerful distributed database solutions offering scalability, fault tolerance, and high availability for large-scale data workloads. ScyllaDB excels in performance, scalability, and ease of use, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring low latencies and high throughput. However, Cassandra's mature ecosystem, community support, and open-source make it a compelling option for organizations looking for a proven and reliable distributed database solution.


 4 Ratings & 4 Reviews
4 Ratings & 4 Reviews