MongoDB and Cassandra are two of the prominent NoSQL databases and we will be comparing both on different parameters. In this quick comparison, we'll explore the key differences between them by examining their respective strengths in data modeling, scalability, query language, and more.
On one hand, MongoDB is known for its flexible document-based data model and powerful querying capabilities. On the other hand, Cassandra is a distributed, masterless database with a focus on high availability and linear scalability. Let’s understand more in detail.
MongoDB vs. Cassandra: An Overview
MongoDB is an open-source, document-oriented NoSQL database that provides high performance, high availability, and easy scalability. It stores data in flexible and JSON-like documents which makes it suitable for a wide range of applications and enables developers to work with data intuitively. MongoDB's features include support for ad-hoc queries, indexing, aggregation, as well as horizontal scalability.
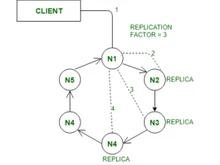
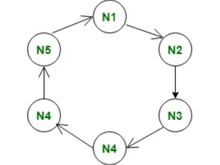
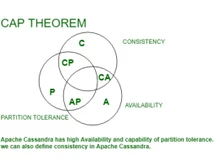
On the other hand, Cassandra is a highly scalable, distributed NoSQL database designed for handling large amounts of data across multiple commodity servers. This helps provide fault tolerance. Apart from that, it employs a decentralized architecture and uses a masterless design to ensure no failure. Cassandra is well-suited for high write throughput as it offers support for linear scalability.
MongoDB vs. Cassandra: Key Differences
Here are a few major differences between MongoDB and Cassandra below:
- MongoDB and other MongoDB alternatives are document-based, using BSON format while Cassandra is a wide-column store, organizing data into rows and columns.
- MongoDB uses MongoDB Query Language (MQL), which supports expressive querying and aggregation. However, Cassandra uses Cassandra Query Language (CQL), which is similar to SQL.
- MongoDB supports vertical scaling through sharding to distribute data across multiple servers. Whereas Cassandra and a few Cassandra alternatives support horizontal scaling to achieve linear scalability by adding more nodes to the cluster.
MongoDB and Cassandra: In Terms of Features
Here's a detailed comparison between MongoDB and Cassandra based on different features including partitioning, data format, query language, concurrency, mobile support, and more. Let’s understand them in detail below:
- Query Language: MongoDB uses MQL to support a wide range of querying and aggregation operations. Contrarily, Cassandra uses CQL, which is similar to SQL for querying and is tailored to Cassandra’s data model.
- Data Format: Cassandra stores data in a structured format based on column families and rows. MongoDB, on the other hand, stores data in BSON (Binary JSON) format, supporting a rich and flexible data structure.
- Concurrency: Cassandra employs a tunable consistency model and supports concurrent read and write operations. Whereas MongoDB uses a reader-writer lock at the database level for concurrency control.
- Partitioning: MongoDB supports horizontal partitioning of data through sharding based on a specified shard key. Whereas Cassandra uses consistent hashing to distribute data across the cluster. This provides automatic partitioning and re-balancing.
- Transactions: Cassandra traditionally did not support multi-record transactions, but now it has introduced lightweight transactions and batch transactions. In contrast, MongoDB supports multi-document transactions and distributed transactions.
- Mobile Support: MongoDB offers a suite of mobile development tools, including MongoDB Realm for offline mobile data synchronization. Whereas Cassandra does not have native support for mobile development.
- Native Data Visualization Tool: Cassandra doesn’t have a native data visualization tool, but it integrates with third-party visualization tools and BI platforms. MongoDB, however, provides MongoDB Charts for native data visualization, allowing users to create and share visual representations of their data.
MongoDB vs. Cassandra: Data Model
MongoDB uses a flexible document-based data model to store data in JSON-like documents. On the other hand, Cassandra follows a distributed wide-column store data model to organize data into rows and columns.
MongoDB or Cassandra: Basic Storage Unit
When it comes to the Basic Storage Unit, Cassandra organizes data into column families and rows, with each row as the basic unit of data. On the other hand, MongoDB stores data in collections, where each document is a basic unit of data.
MongoDB vs. Cassandra: Supported Programming Language
In terms of support for programming languages, MongoDB supports various programming languages including Java, Python, Node.js, and others. Cassandra on the other hand, supports Java, Python, and C++.
MongoDB and Cassandra: Security
Cassandra provides authentication, fine-grained access controls, and SSL/TLS encryption for secure communication. On the other hand, MongoDB offers authentication, role-based access control, field-level redaction, and encryption for data at rest and in transit.
MongoDB or Cassandra: Cloud Offerings
MongoDB offers a fully managed database service called MongoDB Atlas, available on major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Whereas Cassandra offers a managed service called DataStax Astra, as well as integration with various cloud platforms through third-party services.
MongoDB vs. Cassandra: Aggregation Framework
Cassandra provides limited aggregation capabilities through CQL, including basic aggregate functions and grouping operations. On the other hand, MongoDB offers a powerful and expressive aggregation framework for data analysis and manipulation, supporting pipeline-based aggregation operations.
Verdict: Cassandra vs. MongoDB
In summary, MongoDB and Cassandra are different in their data models, query languages, scalability approaches, high availability mechanisms, and consistency models. MongoDB's document-based model and expressive query language make it well-suited for applications with flexible data structures and complex querying needs. On the other hand, Cassandra's wide-column store and decentralized architecture excel in providing linear scalability and continuous high availability. Apart from that, MongoDB excels in flexibility and rich querying, and Cassandra stands out for its linear scalability and fault-tolerant design. Both databases offer unique strengths, and each depends on the use case and architectural preferences.


 4 Ratings & 4 Reviews
4 Ratings & 4 Reviews