We will understand the key differences between two essential components of the Hadoop ecosystem, which are HBase and Hive. HBase is a distributed, scalable NoSQL database designed for real-time, random access to massive datasets, while Hive serves as a data warehousing infrastructure for querying and managing large datasets using SQL-like queries. We will compare both of them based on parameters like architecture, functionality, use cases, performance characteristics, and more.
HBase and Hive: An Overview
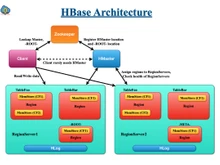
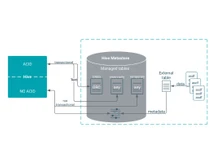
Apache HBase is an open source, distributed, scalable, and highly available NoSQL database that runs with the help of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). It is modeled after Google's Big Table and is designed to provide real-time, read/write access to large volumes of structured data. This makes it suitable for applications requiring low-latency data storage and retrieval, including social media platforms, financial services, and monitoring systems.
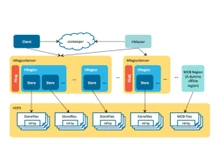
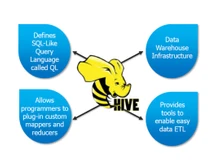
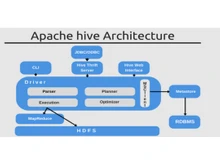
On the other hand, Apache Hive is a data warehouse infrastructure that is also built on Hadoop for providing data summarization, query, and analysis. It supports querying and managing large datasets within distributed storage using HiveQL (a SQL-like language). Hive is used for complex analytics, ad-hoc querying, and reporting on structured data. It, therefore, helps in data processing and analysis within big data environments.
Apache Hive vs. Apache HBase: Key Differences
- HBase is a NoSQL database, optimized for massive datasets, whereas Hive acts as data warehousing, specialized in querying & managing large datasets using SQL-like queries.
- Hive and other similar Hive alternatives use a traditional relational model with tables, columns, and SQL-like querying. On the other hand, HBase follows a wide-column store model, enabling flexible columnar key design.
- HBase and other HBase alternatives provide functionalities for cell-level updates, versioning, and in-memory caching. Whereas Hive supports complex analytics, ad-hoc querying, and data summarization.
- Hive is optimized for batch processing, resulting in higher latency, whereas HBase is designed for low-latency data access, making it suitable for real-time applications.
- HBase requires additional tools or APIs for SQL-like querying, whereas Hive supports SQL-like querying using HiveQL, offering a familiar interface for data analysis and reporting.
HBase and Hive: In Terms of Features
Listed below are a few differences between HBase and Hive based on features like the Replication method, SQL support, Indexing, Hadoop Integration, and more.
- SQL Support: HBase does not have native SQL support and requires additional tools or APIs for SQL-like querying. On the other hand, Hive supports SQL-like querying using HiveQL.
- Indexing: HBase supports automatic and manual indexing for efficient data retrieval and query performance, while Hive supports automatic indexing for improved query performance.
- Replication Methods: HBase supports data replication through Hadoop's HDFS replication mechanisms and provides region replication for fault tolerance. On the other hand, Hive leverages Hadoop's replication and fault tolerance for data redundancy.
- Integration with Hadoop: Both HBase and Hive are part of the Hadoop ecosystem and can be integrated with Hadoop for distributed data processing.
- Database Models: HBase follows a wide-column store model like Big Table, allowing for flexible columnar key design. Hive, on the other hand, uses a traditional relational model with tables, columns, and SQL-like querying.
- Architecture: HBase is an open source, distributed, non-relational database modeled after Google's Big Table, designed to run on a Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). Hive is built on Hadoop for querying and managing large datasets in distributed storage.
Apache Hive vs HBase: Consistency Level
HBase offers strong consistency for read and write operations, ensuring that all clients see the same data at the same time. In contrast, Hive, being a data warehousing solution, provides minimal consistency that is required for analytical queries.
Apache HBase vs Hive: Processing
HBase is designed for real-time, random read and write access to huge datasets. It is suitable for applications requiring low-latency data access. Whereas Hive supports batch processing of large datasets and is used for query as well as analysis.
Apache Hive vs HBase: Database Types
HBase is a NoSQL, wide-column store database that stores data in tables indexed by a row key, column key, and timestamp. On the other hand, Hive is a data warehouse system for querying and managing structured data.
HBase or Hive: Use Cases
HBase is used in applications requiring real-time access to large data sets, such as social media platforms, financial services, and monitoring systems. In contrast, Hive is commonly used for data analysis, reporting applications, and ad-hoc querying.
HBase and Hive: Latency
HBase is optimized for low-latency data access, making it suitable for real-time applications. On the other hand, Hive is designed for batch processing and has higher latency compared to HBase for real-time data access.
HBase or Hive: Query Performance
HBase provides high-performance random read/write access to large datasets but is not much efficient in executing complex analytical queries. Hive, in contrast, is designed for complex analytical queries and provides optimized performance for data analysis and batch processing.
HBase and Hive: Support for Functionality
HBase provides functionalities for real-time, random access to large datasets, including cell-level updates, versioning, and in-memory caching. Hive, in contrast, provides functionalities for complex analytics, ad-hoc querying, and data summarization.
Verdict: HBase and Hive
In summary, HBase stands out in providing real-time, random access to extensive datasets, making it ideal for applications requiring low-latency data retrieval, such as social media platforms and monitoring systems. On the other hand, Hive serves as a robust data warehousing solution, specializing in complex analytics, ad-hoc querying, and reporting on structured data. Both of them play crucial roles within the Hadoop ecosystem, with HBase catering to real-time data needs, and Hive focusing on batch processing and analytical queries.


 5 Ratings & 0 Reviews
5 Ratings & 0 Reviews