Redis and DynamoDB are both powerful database systems with distinct features and strengths. Redis is an open-source, in-memory data structure store known for its high performance and flexibility, while DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It offers seamless scalability, low-latency performance, and a flexible data model. Here, we will be comparing Redis and DynamoDB based on different parameters like features, data storage, scalability, integration, and others.
Redis vs. DynamoDB: An Overview
Redis is an open-source, in-memory data structure store known for its high performance and flexibility. It functions as a key-value database, supporting various data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, and sets. Apart from that, Redis is commonly used as a caching mechanism, message broker, and real-time data analytics solution, valued for its speed, simplicity, and usage across different use cases.
However, DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database software provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It ensures seamless scalability, low-latency performance, and a flexible data model, making it suitable for various applications. It is known for its seamless integration with other AWS services. Apart from that, DynamoDB is a popular choice for applications requiring high availability, reliability, and the ability to handle large amounts of data.
Redis vs. DynamoDB: Key Differences
Here are a few key differences between Redis and DynamoDB:
- DynamoDB and other DynamoDB alternatives store data on disk with optional in-memory caching, while Redis is an in-memory data store.
- Redis is open source, allowing users to host and manage it themselves, while DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- DynamoDB seamlessly integrates with other AWS services, providing a unified environment for building applications, whereas Redis can also be integrated with various cloud services but requires additional configuration and management.
- Redis supports a wide range of data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, and more, offering greater flexibility in data modeling. However, DynamoDB is designed to work with a key-value and document data model.
- DynamoDB offers seamless and automatic scalability, handling large amounts of data and traffic, while the scalability of Redis and a few Redis alternatives depends on the infrastructure it is hosted on.
Redis and DynamoDB: In Terms of Features
Here are some of the major differences between Redis and DynamoDB based on features like Querying, Caching, Backups, Database Model, and more.
- Querying: Redis provides basic querying capabilities through commands such as GET, SET, HGET, HSET, etc., and supports limited search functionalities through modules like RediSearch. However, DynamoDB offers flexible querying using the Query and Scan operations along with support for secondary indexes and conditional operations.
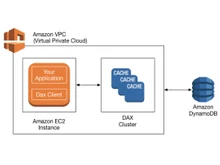
- Caching: Redis is widely used as an in-memory caching solution due to its fast read and write operations, data expiration, and support for eviction policies. On the other hand, DynamoDB is used for caching through techniques like DAX (DynamoDB Accelerator) which provides an in-memory cache for read-heavy workloads.
- Transaction Support: Redis supports transactions through MULTI/EXEC commands, enabling atomic operations for a set of commands. On the contrary, DynamoDB provides ACID transactions through its transactional APIs, ensuring consistency and isolation across multiple operations within a single transaction.
- Backups: Redis supports backups through snapshots and AOF. Apart from that, it also offers the ability to create backups using tools like Redis-CLI and third-party solutions. DynamoDB, on the other hand, provides automated backups with adjustable recovery windows and enables on-demand backups, along with the capability to restore to specific timestamps within the backup retention period.
- Security: Security features in Redis include SSL/TLS encryption for data transmission and access control through password authentication and virtual private cloud (VPC) integration. On the other hand, DynamoDB supports encryption at rest, fine-grained access control, and integrates with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for security.
Redis vs. DynamoDB: Latency
Redis is an in-memory data store and is designed for low-latency data access. It offers incredibly low read and write latencies, making it suitable for real-time applications. Similarly, DynamoDB also provides low latency for read and write operations but with SSD storage.
Redis or DynamoDB: Performance
Redis is known for its exceptional performance due to its in-memory storage and single-threaded nature for command execution. However, DynamoDB provides predictable and consistent performance, with the ability to handle high-throughput applications.
Redis and DynamoDB: Availability & Durability
Redis provides high availability through its built-in replication and clustering features. However, it doesn't have built-in durability as it primarily relies on snapshots or AOF (Append-Only File) for persistence. DynamoDB offers high availability and durability by replicating data across multiple Availability Zones (AZs) within a region, ensuring resilience against component failure.
Redis or DynamoDB: Scalability
Redis provides horizontal scalability through its clustering and partitioning mechanism, allowing data distribution across multiple nodes. On the other hand, DynamoDB offers seamless scalability by adjusting read and write capacity units and supports auto-scaling to handle varying workloads.
Redis vs. DynamoDB: Use Cases
Redis is well-suited for use cases such as caching, session management, real-time analytics, pub/sub messaging, and leaderboard applications. DynamoDB, on the other hand, is ideal for scenarios like web and mobile applications, gaming, IoT, user profiles, and time-series data.
Redis and DynamoDB: Database Model
Redis is a key-value store that supports various data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, and more, enabling complex operations on these data types. DynamoDB, on the other hand, is a NoSQL database that offers key-value and document data models and supports rich querying capabilities using secondary indexes.
Redis or DynamoDB: Architecture
Redis follows a single-threaded, event-driven architecture and is often used as a data store, message broker, and cache. DynamoDB, in contrast, is a fully managed, multi-tenant service designed for high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability, running on the AWS infrastructure.
Redis or DynamoDB: Pricing
Pricing for Redis depends on the chosen service provider and the allocated resources (e.g., memory size, networking, and additional features). On the contrary, the pricing of DynamoDB is based on provisioned throughput capacity, on-demand capacity, and additional features such as global tables and backup storage costs.
Verdict: Redis vs. DynamoDB
In conclusion, Redis and DynamoDB are two distinct database solutions that have different features and capabilities. Redis, on the one hand, is an open-source, in-memory data store, that offers the utmost flexibility with support for various data structures and higher control over data management. However, DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service that prioritizes seamless scalability, low-latency performance, and robust integration with other AWS services. In short, both Redis and DynamoDB cater to differing use cases, aligning with different infrastructure needs and levels of management complexity.


 5 Ratings & 0 Reviews
5 Ratings & 0 Reviews