From a simple boot up to browsing the Internet, everything is possible due to the presence of storage devices like hard disk drives or SSDs.
Each storage device has its own advantages and disadvantages. This blog discusses what storage devices are, the types of storage devices over the decades and their working so that you can better understand the available storage solutions’ options in the market.
What is Storage Device in Computer?
A storage device is a hardware component that may be connected internally or externally to any computing device or a server to store information and instructions. These instructions can be processed on either a temporary or permanent basis.
External or internal storage devices can also be called a storage medium sometimes. The medium can be used to compute results based on instructions, or it can be simply used to transfer or extract information.
Initially, storage devices were based on magnetic tape and punch cards. Later, they were replaced by floppy disks and compact discs to store binary information in digital formats. Now, HDDs and SSDs are the popular options.
What is the Use of Storage Device?
A storage device enables users to securely store data and applications on a computing device. It can also be used to porting information and transferring it from one device to another.
You can access (write/read) the data anytime and retain it for either short-term or long-term depending on your needs. The ability to store large amounts of information in a small device makes sharing process easy.
How Do Storage Devices Work?
There are several types of storage devices and each works through a separate method. The ways in which secondary storage devices could store the information are discussed below.
- Magnetic storage devices
These devices use a mechanical device known as a drive that connects to the computing device. The disk (cartridge or media) coated with iron oxide stores the information and is inserted into the drive. The drive rotates the disk at high speed via motor.
As iron oxide is ferromagnetic in nature, it gets permanently magnetized when exposed to a magnetic field. The stored information is accessed by the drive using tiny devices called read/ write heads that contain electromagnets. The signal created in the coil by the varying magnetic field in the core of the electromagnets is sent to the computer as binary data. This is transferred and converted to machine code.
- Flash memory devices
Flash memory devices contain an array of flash memory cells. The grid of rows and columns have two transistors separated by a thin oxide layer at every intersection. One transistor is referred to as a floating gate, while the other is called a control gate.
When the floating gate is connected to the row through the control gate, the cell has a value of 1. When an electrical voltage charge is applied to the floating gate, a barrier between the control gate and the floating gate is created. If the flow of charge through the gate drops below the 50 per cent threshold, the value becomes 0. With this technique, you can write and rewrite complete blocks or chip areas at once.
- Optical storage devices
A low power laser beam encodes digital data on a laser or optical disk as tiny pits in a spiral track on its surface. By precisely focusing magnetic beams, you can condense huge amounts of data in a tiny space on the optical disks of plastic. A laser scanner reads these pits as the varying intensity of light reflected from the pits converts them into electric signals.
- Online storage
In cloud storage, you abstract the storage resources from physical hardware. For instance, virtualization enables storage to be pooled together in a data lake which can be accessed by users as one repository in a virtual space.
- Paper storage
In the case of paper storage, a programmer would write a program by hand and use a punch card machine to create a stack of punched cards. These cards were fed into a card reader connected to a computer to input the program. The sequence of holes got converted to digital data.
Suggested Read: SAN vs. NAS vs. DAS Storage: Which One You Choose
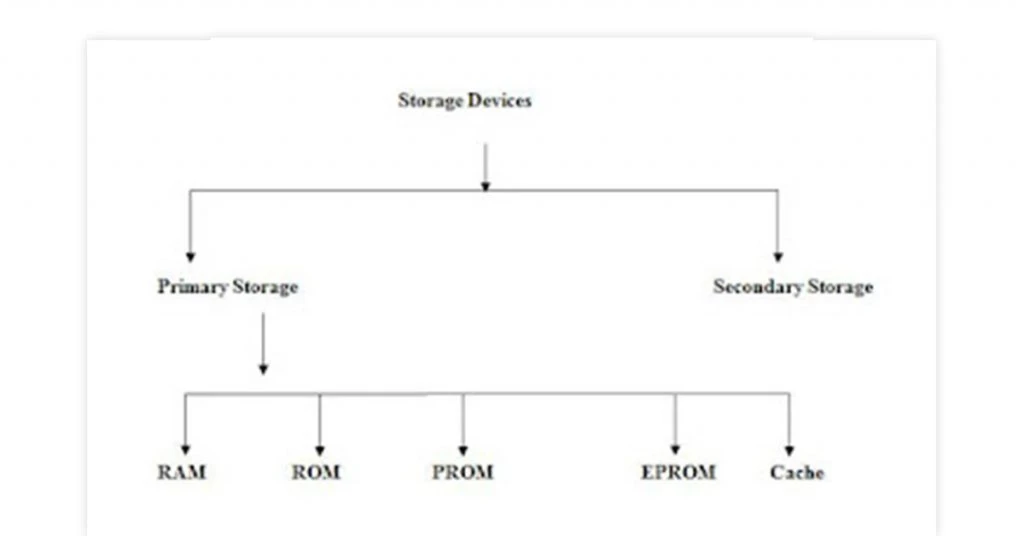
Wat are the Types of Storage Devices?

- Temporary Storage: RAM, ROM, Cache Memory
- Permanent Storage: Magnetic, Optical, Flash & Online Storage
Computer storage devices can be temporary or permanent. Several types of storage devices are discussed here.
- Temporary Storage
Temporary storage includes random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), and cache memory. These are primary storage options in a computer and provide quick access to data in use at any point.
RAM stores volatile data that acts as the working memory for CPU. The data disappears after power is removed. It improves performance and ensures faster loading speed of apps. Common storage device types include SRAM (static), DRAM (dynamic), SDRAM (synchronous dynamic). 8 GB RAM is considered sufficient for simple functions.
ROM stores non-volatile data that stays even after power is turned off. You can only read from it and is often used to power up the system. Two main types of ROM are PROM and EPROM.
Cache memory is small storage embedded in the processing chip of CPUs. This helps in faster processing of instructions.
- Permanent Storage
Common types of permanent storage devices of computers include magnetic storage, optical storage, flash storage. These are considered secondary storage devices of computers.
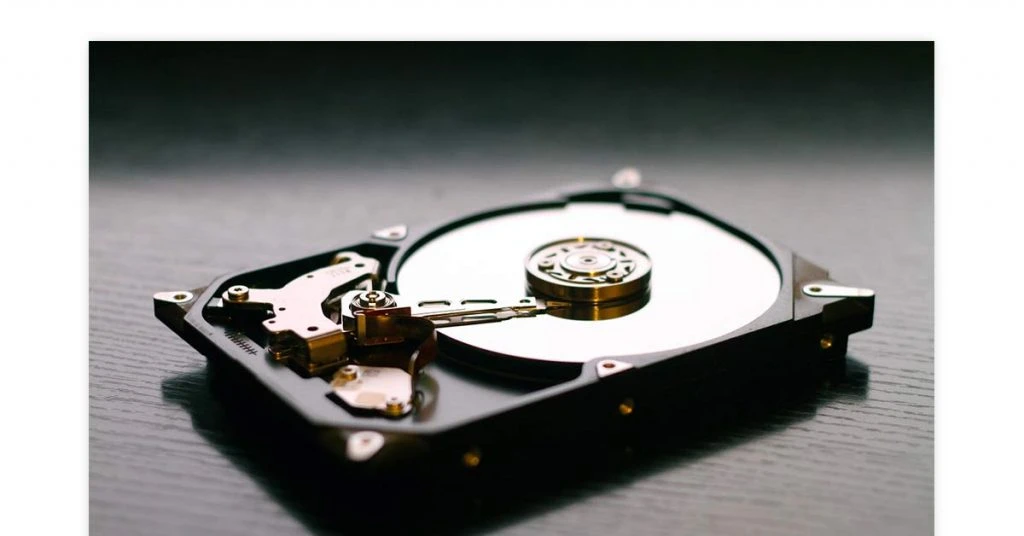
Magnetic storage is a type of non-volatile memory that can store substantial amounts of video, audio, and other data. It provides fast retrieval but can slow down with time. Moreover, it is susceptible to magnetic fields and can get damaged if not handled correctly.
A hard disk is a popular storage device in this category. Other examples of magnetic storage are floppy disk, tape cassette, magnetic card, and super disk.
Optical storage devices have high data stability and mass storage capacity. These secondary storage devices offer low cost per bit of storage, but the overall cost is higher than other options. They are not vulnerable to data loss like volatile memory and cannot be damaged easily either.
Flash storage devices do not have moving parts, require less power and are portable. They have high transfer speed and are not prone to scratches. The content can be overwritten in secondary storage devices like SSDs, pen drives, SD cards, multimedia cards, and memory cards that are based on flash technology.
Online storage enables users to upload data across internet channels that get stored at remote data centers. It is easy to move from one computer to another. However, cybersecurity is a concern and needs to be taken care of with effective measures.
Suggested Read: Top Open Source Document Management Systems for Electronic File Storage
Why Rely on Hitachi Vantara’s Mid-Range Storage Solutions?
Hitachi Vantara’s mid-range storage solutions come with Hitachi legacy and trust that act like a workhorse, no matter what your workload is. Moreover, its 100% data availability guarantee protects your applications and data. Let’s find out other reasons that make these mid-range storage solutions highly reliable.
- Powerful Performance
Hitachi Vantara’s enterprise and mid-size solutions offer advanced data reduction technology that accelerates a business’ performance by freeing up 75% of storage capacity across the entire environment. Additionally, the client’s performance can be further enhanced with easy setup & configuration, rapid provisioning, and accelerated installation. Moreover, all this comes at an approachable cost in the new midrange storage options.
- Quickly Adapts to Changing Organizational Needs
Hitachi Vantara’s mid-range storage solutions are specially designed for a cloud centric and data driven world. This range of storage solutions can be easily tailored to suit your storage environment, irrespective of whether you are an entry level or enterprise level enterprise.
In fact, Hitachi Vantara’s latest VSP E series has been created with the forward momentum, which keeps you prepared for tomorrow. Moreover, your business will never be locked into a specific storage technology, platform, or even scale.
- Optimize Storage Solutions
As your business grows, your dependency on storage technologies will increase. With Hitachi Vantara’s storage solutions, you will get more flexible options while selecting the media that helps you meet your budget, reliability, and unique performance requirements.
As your business scales, you can mix different storage resources like NVMe, spinning disk drives, and more to optimize and align with your cost and performance needs.
- Helps in Delivering Resilience
Irrespective of the Hitachi Vantara’s storage solution that you choose, be it VSP 5600 or Hitachi VSP E590, one thing that you will always get in common is Hitachi’s legendary resilience. For instance, even VSP E series systems come with their global cache architecture technology.
This technology ensures that the hosts keep on working effectively by shifting workloads among different controllers, even under some of the most demanding workloads. In addition to this, Hitachi’s storage solutions maintain your peak performance by freeing up storage controller CPUs. This is done using a new hardware assisted data reduction card that very well handles compression.
Difference Between Cloud and Virtual Storage
Since secondary memory is not easily scalable, users have moved to the cloud and virtual storage options.
Cloud Storage
Cloud service providers (CSPs) like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft enable users to store their data in a physical device that is located at a data center owned by these providers. The internet is used as a way of abstracting, sharing, and pooling storage resources.
CSPs maintain storage resources and provide the users with whatever amount of space they need if they pay for it. The choice of cloud may be public, private, or hybrid. Data migration is possible through a network of LAN, WAN, API, VPN, and containers.
You can have three different ways of formatting the storage, namely, blocks, objects, and files, that are usually combined in a unified solution. The format is chosen depending on the needs and is different for various types of data storage.
Block storage is preferred for high-performance workloads where you need fast speed and low latency storage. Object storage is used for quick access in cloud-native apps as the objects are uncompressed and unencrypted.
File storage is common in NAS (network-attached storage) systems and is used for organizing and representing data in an easy-to-understand way.
Virtual Storage
Some businesses choose virtual storage in which the storage is pooled from different network devices into a single device that exists in a virtual environment. By making all the storage capacity available to every user, individuals are not limited to storage on a single computer.
These storage products are offered by companies like NetApp, IBM, and Hitachi to provide high storage capacity and scalability for archiving, backup and recovery.
You don’t need to increase the storage through portable storage media for users working with large apps. They can access excess storage of those users who do not require high storage capacity for their tasks.
Examples of Computer Storage Devices
Storage devices of computers can store large amounts of digital data in a small physical space that makes backing up data and sharing simple.

Examples of Magnetic Storage Devices
Hard Drive Disk
A hard disk drive or hard drive (HDD or HD) is a common storage device present in computers for backup and archiving purposes. It is a type of magnetic storage device capable of storing operating system (OS) files, software applications, and other documents with text, videos, audios, and images. Typical storage capacity varies from 500GB to more than 4TB.
Magnetic Tape
Magnetic tapes started being used in the last century due to their low price and large storage capacity. Data can be written along both length and breadth. However, they are slow when compared to other modern storage solutions.
Floppy Disk
Before hard disks, floppy disks (FD) were the popular magnetic storage devices that could store data. Also called diskettes, these disks were available in 8-inch (203 mm), 5.25-inch (133 mm), and 3.5-inch (90 mm) versions over the years. They typically provide up to 240MB of space.
Examples of Optical Storage Devices
Compact Disc
A compact disc (CD) is a storage medium for music and small amounts of computer data based on optical technology. The storage capacity is usually around 700MB.
It is of three types, namely CD-ROM (read-only), CD-R (writable), and CD-RW (rewritable). The information is read and written through a laser as CDs rotate at a constant speed.
DVD and Bluray Disc
Digital versatile disc (DVD) and Bluray disc (BD) have a higher storage capacity than CDs of the same physical size. Large amounts of data, including HD video, can be stored easily.
They use a finer laser due to higher density and have a usual storage capacity of 4.7GB (DVDs) or 25GB to 128GB (bluray discs).
Suggested Read: What is a Utility Program & What Are Its Functions?
Examples of Flash Memory Devices
USB Flash Drive
USB flash drive is a small portable device with an integrated USB interface. You can plug it into a computer’s USB port and easily move files from one device to another.
It has a higher storage capacity than optical storage devices, typically between 8GB to 256GB. It is also faster and more reliable. Its other names include pen drive, jump drive, memory stick, thumb drive, and USB stick.
Secure Digital Card
A secure digital card (SD card) is a rectangular shaped device that is available in various sizes and capacities for different devices, including mobiles and cameras. Common options include full-size SD, mini-SD, and micro-SD cards. Storage capacity often varies between 2GB to 32GB.
Solid-State Drive
A solid-state drive (SSD) is nowadays being used in combination as well as for the complete replacement of HDDs in laptops, PCs, etc. It comes in both external and internal configurations.
As it offers lower capacity compared to a similar priced HDD, it is more common among expensive devices. It uses NAND flash memory, and its benefits include low power consumption, small form factor, high read/ write speed, high reliability, and noise reduction. Storage varies from 120GB to over 1TB.
Examples of Online/Cloud Storage
AWS S3 Storage
As cloud computing gains popularity, the adoption of cloud storage services for different types of data storage is also increasing. Cloud storage is a scalable solution for storing substantial amounts of data and requesting resources from the vendor as the need grows.
The cloud vendor has a collection of remote servers for hosting and management of services that can be accessed by the devices over a network. A popular example for cloud storage is Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 storage, in which users can store data virtually instead of other available secondary storage devices of computer.
Examples of Paper Storage
Punch Card
It is a paper card with hand-made or machine-made, punched, or perforated holes. Punch card was entered into a computer to store and access data.
Conclusion
Data can be lost due to several reasons like power failures, cyberattacks, accidental deletions, physical damage, or even natural disasters. Hence, you must keep backups in your secondary storage devices.
Now that you know what a storage device is, you can decide better. Businesses are moving to cloud storage as it is reliable, offers scalability, and better performance.
Suggested Read: Google Drive Vs Dropbox Vs OneDrive: Best Google Drive Alternative 2022
FAQs
Why is storage needed?
Storage devices are required to store and access information on a computing device. Internal computer storage devices are required for the most basic functions, including starting a computer and working with an OS to access I/O devices. It is also necessary to run applications on the OS.
Why so many different storage devices?
Depending on the device size and applications, different computer storage devices provide advantages like faster access, portability, less vulnerability against damage, higher capacity, etc. Storage devices also evolved with technology improvements.
What is storage location in a computer?
Primary storage is the computer’s core storage and is present on the motherboard. Secondary storage devices may or may not be removable and are present within the computer case.
Which storage device is best?
The choice of computer storage device depends on your budget and needs. The best storage devices available in the market today include SSDs, HDDs, USB drives, etc.
Which storage device has the largest holding capacity?
A hard disk is a storage device with a large holding capacity. With cloud storage, the capacity can be expanded as per requirement.
What are 4 types of storage devices?
The four types of storage devices are magnetic storage devices, optical storage devices, flash storage devices, and online storage devices.
What are the storage devices?
Storage devices are hardware components that can store data and make it accessible to the user via the computing device.
What is the most popular secondary storage device these days?
Most popular secondary storage devices include hard disk drives and SSDs for computers these days.
How to view all storage devices?
To view all connected storage devices, go to Settings> Storage. In the More storage settings section, click View storage usage on other devices.
Are storage devices input and output devices?
No, storage devices do not get input from the user directly and they do not display the output to the user. They communicate with the CPU.
What are the latest storage devices available?
Latest storage devices include SSDs and cloud/ virtual storage.
Related Categories: Cloud Storage | Server | Network Devices | Wireless Access Point | Data Security Solutions
Rajan is pursuing CA with a keen interest in trends and technologies for taxation, payroll compliances, Tally Accounting, and financial nuances. He is an expert in FinTech solutions and loves writing about the vast scope of this field and how it can transform the way individuals and businesses... Read more