Understanding SaaS: Commonly Used SaaS Terms & Acronyms

Software as a Service industry is expected to reach USD 716.52 Billion in 2028.
This is majorly because big, small and medium, every business type has started adopting and benefiting from the flexibility of SaaS. It allows them to enjoy all the features of the software on a subscription basis, without deploying the software on premises. The SaaS model gives businesses the freedom to start or stop software subscriptions at any time.
However, still there are certain SaaS terms, words, phrases, and jargons that are unknown or probably misunderstood even by the frequent SaaS users.
Common SaaS Terminologies
We have created a glossary with all the major SaaS terms that any business owner, CEO, startup founder, project manager, or any professional should know.
A
Average Customer Life
It is the average duration from the moment your prospect becomes your customer till the time he stops taking your services or cancels the subscription. It helps in defining the duration for which a customer was associated with any subscription-based vendor.
Annual Run Rate Revenue
ARRR is the method of forecasting your next year’s annual revenue or performance based on your last year’s earnings. While calculating this, a company assumes that nothing will change in the coming year, no customers will be added, or no expansion will be made, to assume the minimum revenue they will make.
App Integration
App integration is the process of connecting a business’ existing systems or information to a new application. For instance, you can integrate your customers’ contact information with email marketing systems, rather than creating a separate database for it.
Annual Contract Value
ACV sales term means the average value of your subscriptions or contracts. However, ACV in SaaS might differ on a yearly basis if your company charges a one-time fee in the beginning. The first will involve both, one-time fee and subscription charges.
B
Break Even
Break even happens when a company earns revenue from a customer that is equal to the amount spent on acquiring him.
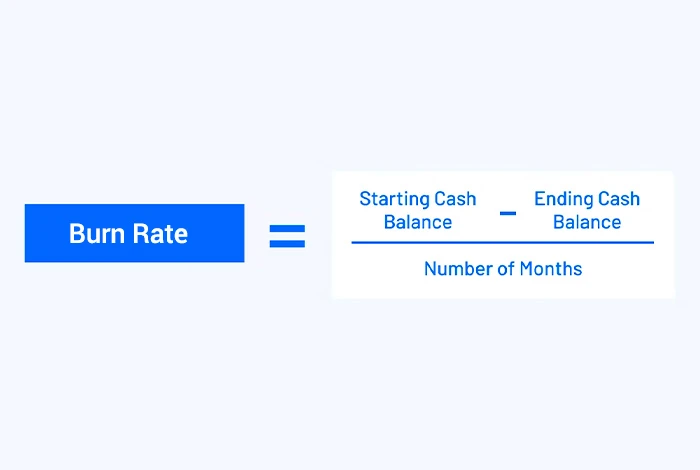
Burn Rate
In SaaS terms, Burn rate is the rate at which an organization spends its initial money or capital before turning into a profitable organization. You can use this formula to calculate burn rate:
C
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a service that allows users to use remote servers to manage, process, and store information over the cloud. Here, instead of buying or creating their own IT infrastructure, users can subscribe to any software.
Customer Retention Rate
It is the percentage of your existing customers who continue with your service and renew their contract or subscription. It will help businesses understand what keeps their customers with the company, and what services or packages are renewed frequently. To calculate Customer Retention Rate, use the following formula:

D
DaaS
DaaS is Desktop as a Service where the service provider hosts a virtual desktop. Users can access these virtual machines and operating systems exactly like using their personal systems through a web browser.
E
Engagement Loop
The engagement loop is a method of keeping your customers and prospects engaged with your services and products so that they keep on taking the next step to gain additional value from your service.
Suggested Read: Tips to Reduce Customer Acquisition Cost and Increase SaaS Conversion
F
Freemium
Freemium is a customer acquisition method where a business offers premium features of the product for free without keeping a time limitation. However, they can put restrictions in terms of the number of users accessing certain features at a given time.
Free Trial
Free trial is another popular customer acquisition approach that offers software for a limited period. The free trial can range from 7 days to 30 days or even more.
G
Go-To-Market (GTM) Strategy
Go-To-Market (GTM) Strategy involves an action plan that tells how an organization would persuade its prospects into buying its products or services. It provides a competitive advantage over others in the market. This strategy is around scaling your business along with increasing repeat customers by offering competitive pricing.
H
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud computing is a combination of both, private and public clouds because businesses can’t entirely rely on the public cloud. It is great for businesses that want to scale and keep their information using the public cloud. But at the same time also want to comply with their data residency laws using a private cloud.
Suggested Read: Popular Quotes on SaaS to Inspire Your Team to Achieve More
I
In-Product Call to Action
This is a marketing term that indicates the next action of your prospects while persuading them towards conversion. Some popular CTAs used are ‘know more’, ‘buy now’, ‘get a call back’, and more.
Suggested Joke:
L
Loyalty Loop
A loyalty loop is a process of offering a positive customer experience and significant value through the product to encourage your clients to keep using your product, extend their subscription, try new features, and scale its use.
Latency
Latency is the time taken while transmitting data from the sender to the receiver. Lower latency facilitates faster data transmission. Moreover, high or low latency also depends on the physical location of the server, the closer the server will be, the lower the latency will be.
M
Migration Costs
These are costs related to data movement that a business must bear while migrating from the existing systems or applications to the cloud. This cost may differ depending on the scale and workload of the migration project.
Monthly Recurring Revenue
MRR is the total revenue that a company can expect from active subscriptions every month. Using MRR, a business can assess its financial condition and make estimates of future earnings based on active subscriptions.
O
Omnichannel Approach
The omnichannel approach is a way to stay connected with your customers across channels, no matter if they are using a mobile, desktop, tablet, or any other smart device.
P
Product Lifecycle
In SaaS terms, Product Lifecycle is the journey of your product through its four stages in the market, introduction, growth, maturity, and eventually decline. These stages help organizations to determine their marketing and sales strategies.
Personalized Customer Experience
Personalized customer experience means curating and delivering personalized messages, emails, custom solutions, etc., to your customers. This helps in increasing customer engagement and indulging in relevant conversations during chat and email support.
Product-Qualified Leads
PQLs are prospective clients who have shown interest in your product or service. This interest can be seen in the form of signups, availing of a free trial, filling in a contact us form, etc.
S
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
SLA in SaaS terms is a document that contains all the information related to what a customer should expect from the service provider. SLA documents are important for service providers to ensure transparency while defining their responsibilities. One should clearly mention things such as uptime, service availability, query resolution time, escalation path, termination terms, payment conditions, methods, and more.
Sign Up-To-Customer Rate
It is the rate at which the visitors that sign up on your website become your customers and pay for your services. According to a report by WordStream, the average sign up to customer rate ranges between 2% to 5%.
U
User Onboarding
As per SaaS terms, user onboarding is the process of getting a new subscriber’s account up and running. This process involves user training, account setup, and integration support for a new user. The main objective of the complete process is to make new users familiar with your product and provide them the complete knowledge of how your software works.
Unified Customer Profile Data
It is a brief profile of your customers that provides you with an overview of their characteristics, activity, preferences, and history. It creates this overview by collecting customer information from multiple sources and then displays it through a single profile.
V
Visitor-To-Signup Rate
This is the proportion of the number of visitors who visited your website to the number of visitors who signed up. This helps organizations in determining how effective your website is in convincing your visitors to sign up for a free plan, free trial, call back, and more. Businesses can calculate the visitor to signup rate using the below given formula:
No. of new subscribers in a month / No. of new visitors in a month X 30 days
Z
Zero Party Data
Zero Data is the data that your customer intentionally shares with your company. This may include their personal demographics, purchase intentions, query, etc. This will help your business to understand what your customer wants and create more personalized experiences.
FAQs
What is the full form of SaaS abbreviation?
The full form of SaaS term is Software as a Service.
What SaaS means?
SaaS definition is a method of offering software on a subscription basis rather than buying or installing it on your systems.
What are the popular SaaS examples?
Some popular SaaS examples are HubSpot CRM software, Salesforce, Slack messaging, ClickUp, etc., among others.
What is SaaS in IT terms?
SaaS in IT terms means delivering software and applications over the internet on a subscription basis. It eliminates the need for a business to create its own IT infrastructure.
How many types of SaaS are there?
There are two types of SaaS businesses, horizontal SaaS business, and vertical SaaS. Horizontal SaaS businesses offer services to diverse clients in multiple industries. However, Vertical SaaS businesses offer services to a niche industry.
What are the parts of SaaS?
Different parts of SaaS are CRM systems, billing systems, marketing automation, customer analytics, etc., among others.
Isha’s writing journey started way back in 2018 when she graduated in the field of Journalism & Mass Communication. Since then, she has been writing for all digital and print marketing assets including blogs, editorial reviews, landing pages, emailers, and more. She has contributed her writings to genres... Read more








.jpg?d=100x100)