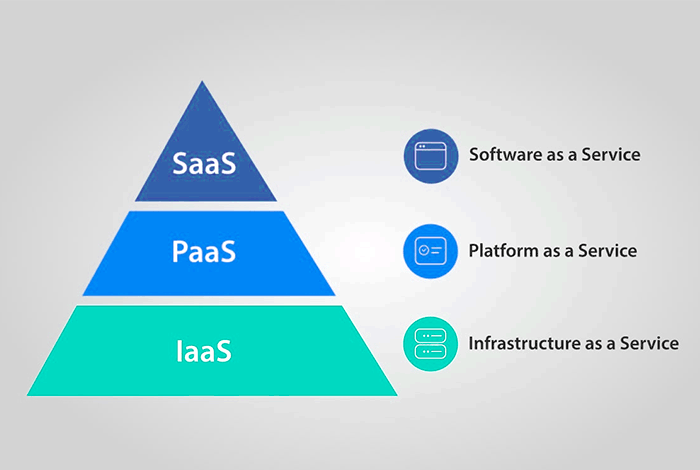
Summary: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are three main type of cloud computing service models. IaaS provides on-demand infrastructure, PaaS provides a platform for application development, and SaaS provides ready-to-use software solutions. But which one is right for you? Let’s discover.
There has been a significant increase in the popularity of cloud computing lately. Due to this, many businesses have started shifting from their traditional on-site IT solutions to using cloud computing services provided as platforms, infrastructures, and software.
If a business wants to shift its operations to the cloud, then it must be aware of 3 essential terms, which are also known as the types of cloud computing service:
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
We will discover the major differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS and also how they are taking the business to the front foot. We’ll examine how these “as-a-service” options can fit your present IT setup and what advantages and drawbacks they bring.
What is IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
Before discussing the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, first, let’s understand what exactly these cloud computing models mean. Read about IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS definition.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) is a flexible cloud solution where businesses manage the IT infrastructure, such as servers, storage, networking etc. through self-service portal. This helps businesses to eliminate the need for costly on-premises hardware and shift them to the cloud.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a platform with built-in tools, programming languages, and services for application development, testing, and deployment. At the same time, it allows the customer to manage applications and data.
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud service where the provider offers software applications over the internet. The customer can access and use these on a subscription without installing or managing any of them on their own systems.
Suggested Read: What Is SaaS? Find Latest SaaS Examples & Trends
Difference Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
| Parameters | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| Delivery Model | Cloud-based | Cloud-based | Cloud-based |
| Users | Network Architects and IT Administrators | Developers | End Users |
| Technical Requirements | Needs technical understanding | Requires some knowledge for basic setup | Little to No Technical Knowledge Required |
| Cloud Support | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| User Control | Highest user control | Low user control | No user control |
| Usage | Pay-as-you go | Pay-as-you go | Subscription-based |
| Operational Cost | High | Minimal | Low |
| Vendor Risk | Low | Medium | High |
| Examples | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform | Heroku, Google App Engine | Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, Dropbox |
Characteristics of IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
The world of cloud computing has given us many options to choose from when it comes to building and deploying applications. IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are three of the most popular cloud computing models that are widely used by businesses of all sizes.
Each of these models has its own set of characteristics that make it unique and suitable for different types of applications. Here’s a brief overview of the characteristics of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS:
Characteristics of IaaS or Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is probably the most flexible out of the three models. It allows businesses to use different computing resources like servers and networking. With IaaS, businesses can manage their operating system, middleware, apps, and data.
- Scalability: Allows you to scale up and down your infrastructure resources as needed.
- Flexibility: With IaaS, you have the flexibility to choose the hardware and software components that best suit your needs.
- Automated IT Services: Automates administrative tasks such as backups and updates, reducing the burden of manual tasks on IT staff.
- Control: Gives you complete control over the infrastructure, operating system, and applications.
- Cost-effective: Runs on a Pay-as-you-use model, which can be cost-effective for businesses of all sizes that must manage their own applications and infrastructure.
Suggested Read: What Differentiates PaaS from SaaS – PaaS Vs SaaS
Characteristics of Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS simplifies the software development process by providing a ready-to-use platform, enabling developers to focus on coding rather than dealing with infrastructure-related issues.
- App Development: PaaS helps with rapid app development and allows developers to quickly create and deploy applications without the underlying infrastructure.
- Flexible: The system uses virtualization technology and helps with flexible resource allocation according to the changing needs of your business.
- Multi-tenant: Multiple users can access the development application simultaneously, enabling collaborative work.
- Web Integration: The system seamlessly integrates web services and databases into development.
Characteristics of Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based service that can be accessed via a web browser and is wholly controlled by vendors, removing the need for in-house IT. This simplifies corporate operations and provides quick access to a fully operating software application.
- Centralized Control: SaaS provides a centralized control system that allows users to access and manage their software applications and data from a single location
- Hosted on a Server: Hosted remotely on a cloud provider’s server eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure and maintenance.
- Accessible Online: Applications are accessed via the Internet which provides convenient accessibility and availability from any location with just an internet connection.
- Automatic Updates: SaaS applications are distinguished by automatic updates, which ensure that the program is always up to date without manual participation.
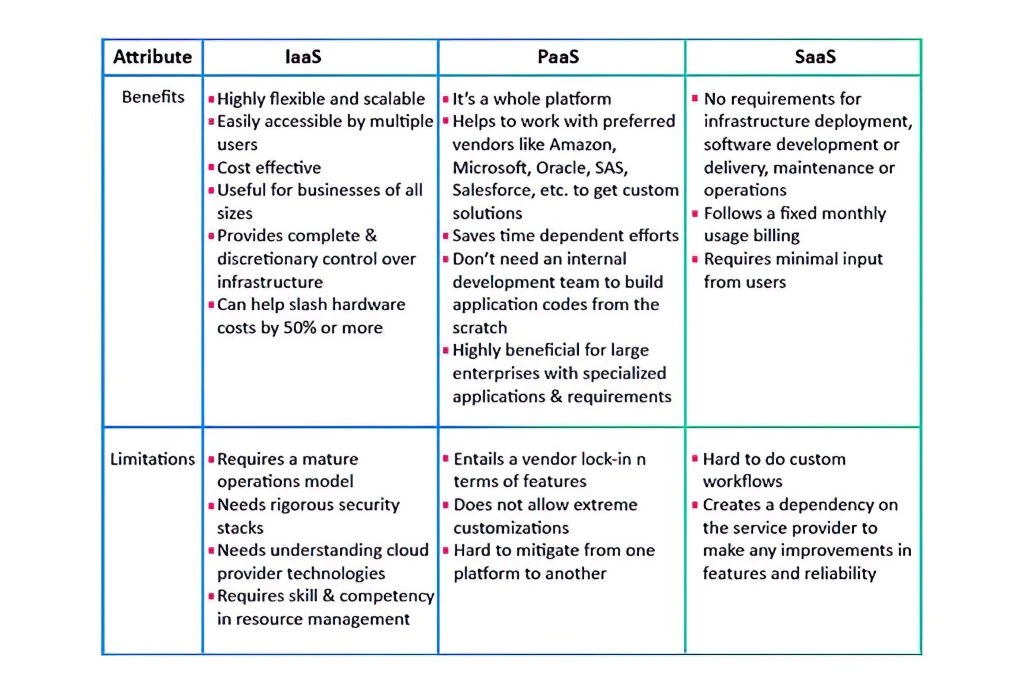
Advantages and Disadvantages of IaaS

IaaS Advantages
IaaS offers various advantages, including:
- A high amount of freedom and customization.
- Enables on-demand scalability of computing resources.
- A low-cost way for organisations to handle their IT infrastructure as compared to in-house.
- Reduces operational costs by outsourcing maintenance and updates to the provider.
- Removes the need for businesses to buy and maintain their own physical infrastructure.
IaaS Disadvantages
When moving to IaaS, there are some restrictions and issues to consider, such as:
- 3rd Party Dependency: Dependent on third-party providers, which can lead to concerns with mobility and lock-in of vendors.
- Requires Internal Training: Shifting to IaaS solutions can be a new challenge, and sometimes it may require internal training to use the platform efficiently, which can be a time-consuming process.
- Security and Data Concerns: As with any cloud-based service, this comes with security and data risks, which can be exacerbated by third-party access.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PaaS

PaaS Advantages:
PaaS offers many advantages for businesses, including:
- Simple scalability and adaptability for growing business demands.
- It enables collaboration among developers and teams in a single environment.
- Increased security and reliability with automatic updates and backups.
- Cost-effective pricing models with pay-as-you-go model.
- Better availability and uptime for apps.
- PaaS helps businesses to focus on application development rather than infrastructure management.
PaaS Disadvantages:
- Vendor Dependency: One disadvantage of using PaaS is the dependency on the service vendor. For example, users may face issues if the vendor experiences downtime or goes out of business.
- Compatibility Issues: Developers need to ensure that their applications are compatible with the PaaS provider’s platform and technology stack. There might be some apps or software that are not compatible with the PaaS platform.
- Security Concerns: Using a third-party service like PaaS can generate security problems. To avoid any data breaches or cyber assaults, you must confirm that the platform fulfils its security standards and conforms to current rules.
- Complex Migration Process: Sometimes, users may face challenges when moving their applications and data to a new PaaS platform. It results in delays and potential disruptions to their business operations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SaaS
SaaS Advantages:
SaaS has its own sets of advantages, including:
- Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection makes SaaS convenient.
- SaaS provides a consistent experience across devices and operating systems.
- SaaS enables businesses to quickly implement new software solutions without the need for lengthy installation processes.
- SaaS providers take care of software maintenance and security updates.
- It offers flexible subscription plans to fit different business needs.
- SaaS allows for collaborative work with remote teams.
SaaS Disadvantages:
- Internet Dependency: Since SaaS applications require an internet connection, they are vulnerable to downtime and interruptions in service. This can have a significant impact on business operations.
- Less Control: With SaaS, users have very limited control over the software. They must rely on the provider to maintain and update the software.
- Limited Customization: SaaS applications are often designed to be general-purpose solutions that meet the needs of a broad range of users. As a result, they may not offer the level of customization that some businesses require.
- Security Concerns: SaaS platforms require users to store their data in the cloud, which can be a security concern for some businesses. While SaaS providers typically have robust security measures in place, data breaches can still occur.
Examples of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
| Service Model | Examples |
| IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Digital Ocean, Linode |
| PaaS (Platform as a Service) | Google App Engine, RedHat, Heroku, OpenShift, Digital Ocean |
| SaaS (Software as a Service) | Google Workspace, Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce, Dropbox, Zoom, Slack, Shopify |
SaaS vs PaaS vs. IaaS Market Share
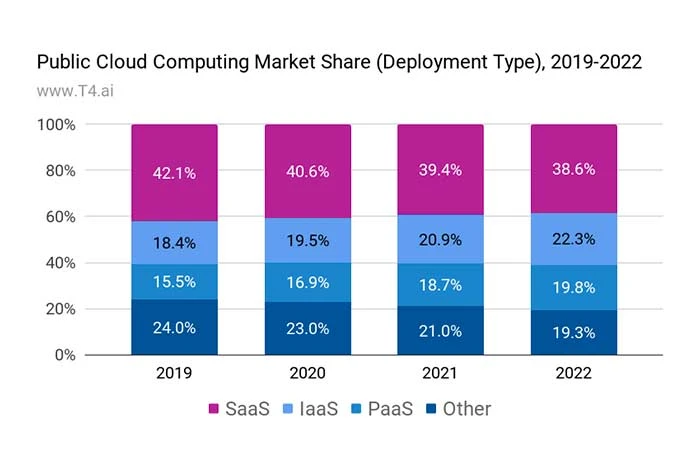
The chart shows the size of the global Cloud Computing Market from 2019 to 2022 and the market share by deployment model.
- SaaS is the most popular service in the cloud computing industry, with a market share of 38.6% in 2022.
- IaaS is the second most popular service, with a market share of 22.3%, followed by PaaS at 19.8% and other categories at 19.3%.
The pattern shows a minor drop in the SaaS model and a rise in PaaS and IaaS, which will likely increase further in the future.
Conclusion
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are all unique cloud computing models with distinctive features to cater to different needs. One provides better control and the other provides easy customization.
It’s essential to understand which one is more essential to your company: authority, customization, or ease. And, once you’ve decided, look for a provider whose values align with those of your firm to increase team efficiency and effectiveness.
So, take the time to weigh the features, characteristics, pros and cons of each option before making a decision that will impact your business in the long run.
FAQs
What are SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS examples?
Some examples of IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) are Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine. PaaS (Platform as a Service) examples include Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Service. SaaS (Software as a Service) examples include Salesforce, Zoom, and Dropbox.
What's the difference between PaaS and SaaS?
PaaS (Platform as a Service) provides a platform for customers to develop, run, and manage applications, while SaaS (Software as a Service) provides access to pre-built software applications hosted on a cloud infrastructure.
Which is better, IaaS or SaaS?
It depends on the specific needs of the user. IaaS is more suitable for users who want more control over the underlying infrastructure. At the same time, SaaS is more suitable for users who want a ready-to-use software without having to worry about managing infrastructure.
What are the five examples of SaaS?
The 5 examples of SaaS are Slack, Shopify, Salesforce, Zoom and Mailchimp.
What is a PaaS example?
A few examples of PaaS include OpenShift, Digital Ocean, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud etc.
What are the 3 benefits of IaaS?
The three major benefits of IaaS are flexibility, cost saving and scalability.
What is the weakness of IaaS?
The weaknesses of IaaS include security concerns, dependency on vendors, limited customization etc.
Shubham Roy is an experienced writer with a strong Technical and Business background. With over three years of experience as a content writer, he has honed his skills in various domains, including technical writing, business, software, Travel, Food and finance. His passion for creating engaging and informative content... Read more