In the evolving world of digital analytics, Google Analytics 4 (GA4) has become a central tool for tracking user behavior across websites and apps. As data privacy regulations tighten, it’s more important than ever to understand how GA4 uses cookies, particularly when it comes to user tracking and identification. This blog will dive into the role cookies play in GA4, how Google uses them, and what changes GA4 introduces to help businesses navigate the complex landscape of privacy and user consent.
How GA4 Uses Cookies to Track Users?
GA4 uses first-party cookies to anonymously track user interactions across a single website or app. Here’s a closer look at how GA4 uses cookies for tracking:
Session-Based Tracking
In GA4, cookies help manage user sessions by storing unique identifiers. Each time a user visits a site, GA4 can recognize their device and browser, allowing it to accurately track the duration and nature of the session without revealing personal information.
User-ID and Anonymous Identifiers
GA4 can also track users with its User-ID feature, which uses unique identifiers assigned by the website or app, helping businesses connect user behavior across sessions and devices. Additionally, GA4 leverages anonymous identifiers to manage data collection in a privacy-conscious manner, ensuring user identities remain protected.
Cross-Platform Tracking
One of the standout features of GA4 is its ability to combine web and app data, offering a unified view of user interactions across platforms. Cookies are essential here to create a consistent user experience and better understand the customer journey.
How to View Cookies In GA4?
Google Analytics 4 or GA4 cookies are set to allow Google Analytics to recognize unique users and sessions and track interactions while enabling data collections such as page views, session duration, and user engagement.
- GA4 cookies are held in the user’s browser and can send data on the user’s interaction with the website back to the server, meaning that Google Analytics can track the interactions. Here is how to find GA4 cookies on your website or application.
- Open a website that has GA4 installed.
- Navigate through the developer console on your web browser and go to the Cookies section.
- Click on the domain where your website resides.
- Look for cookies labeled as _ga.
Suggested Read: How To Check Cookies In Browsers?
Conditions to See GA4 Cookies:
- Open the webpage in a Private/Incognito Window and close all other sites. That way, no more cookies are loaded to mess up.
- Turn off Third-Party Cookie Blocking. Most browsers block third-party cookies by default. Turning this off might make GA4 cookies appear.
- Turn “Do Not Track” and “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” off.
These settings will prevent third-party cookies from loading and therefore you might not see them if you have them on. By following these steps, you should now be able to see GA4 cookies easily.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) Cookies

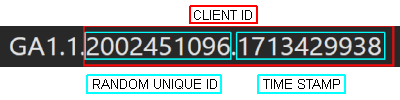
If you enter the CookieScript website from Chrome, you may observe the following GA4 cookies: _ga, _ga_6HZSPS6QTR, and _gcl_au. These are cookies of GA4, though _fbp is of Meta, formerly Facebook. Let’s examine the structure of the _ga cookie more closely to understand more about how GA4 works.
In the _ga cookie, you will be able to see the structure in the following format.
- Name: _ga
- Value: A string composed of letters and numbers. This string uniquely identifies that cookie.
- Issuer: the website you’re accessing
- Expiration Date: Example: 2025-05-23.
The _ga cookie has four parameters:
- Version Number: A numeric value to indicate which cookie format version it is in this case, it is GA1
- Domain Level: is set by default at a value of 1. This is because the new GA4 cookies are sent to the top domain
- Random Unique Identifier: It is a number that is randomly assigned; it is 10-digit long. For instance, 2002451096.
- First Timestamp: It is a timestamp reflecting when the cookie was initially generated. For example, 1713429938.

Taken together, the third and fourth fields make up the Client ID used in this example to which value is stored in the GA4 cookie- 2002451096.1713429938. Google Analytics uses the ID for connecting user activities as well as monitoring their engagement.
GA4 Cookies Across Domains and Devices
GA4 cookies are site-centric by default, so the same cookie is used for tracking whether you are on the primary domain or any of its subdomains. For tracking users across more than one domain, this can be done through:
- GA4 Cookies for Cross-Domain Tracking: This will allow the tracking of users across browsers and devices.
- CMP with Cross-Domain Tracking: A CMP will help manage consent and allow users to be tracked effortlessly across domains
Conclusion
As digital analytics continues to evolve, so too must our understanding of cookies and data privacy. Analytics tools like Google Analytics 4 have taken significant steps to protect user data while delivering valuable insights. By adapting to GA4’s privacy-centric tracking features, businesses can future-proof their analytics strategies in a cookieless world. Embrace GA4’s new model, explore its privacy-focused features, and prepare for the next chapter of data-driven decision-making.
Namrata is a skilled content writer with an expertise in writing marketing, tech, business-related topics, and more. She has been writing since 2021 and has written several write-ups. With her journey with Techjockey, she has worked on different genres of content like product descriptions, tech articles, alternate pages,... Read more